

Ranganath & Blumenfeld (2005) argue that MTL binds novel items together in single representation.STM/LTM distinction or novelty (MTL) and resistance to distraction (frontal) parietal for late probes (Talmi, Grady, Goshen-Gottstein, & Moscovitch (2005) Temporal activation for early probes in serial recall paradigm Increased delay affects recency but not primacy effect.Presentation rate affects primacy but not recency effect.Inferior Temporal = LT visual pattern recognition deficitsīehavioral data confirming STM/LTM distinction Damage to Medial Temporal produced LTM deficits while leaving STM in tact.
Secondary Visual Pathways: Dorsal and Ventral Streams Localization of function: do discrete circuits carry out different functions?.Temporal: Hearing, language comprehension.Frontal: Self-awareness, planning, voluntary movement, emotional control, speech, working memory.

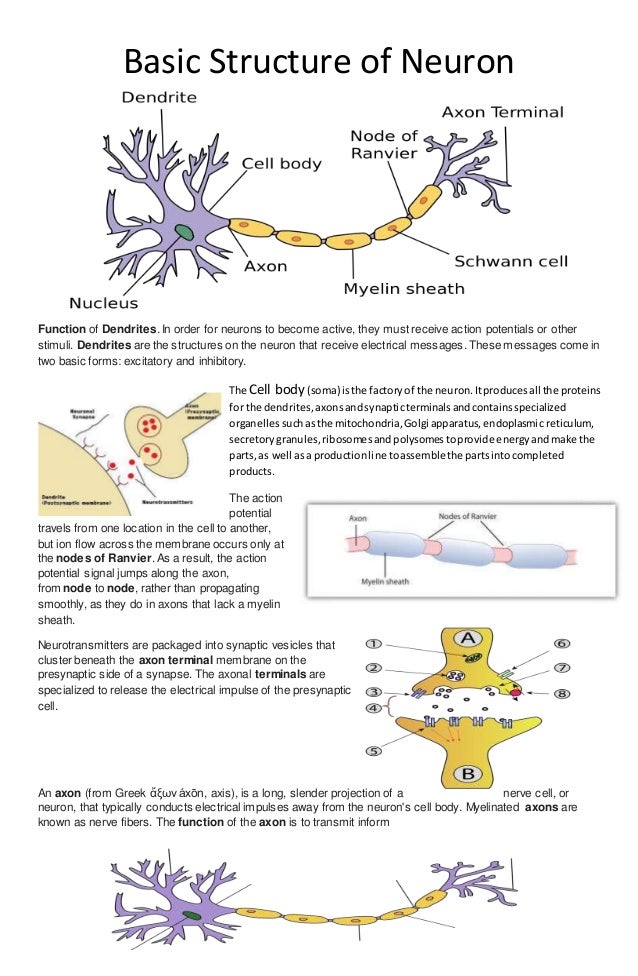
Consists of left and right hemispheres. Cortexrefers to the outer covering of the brain. Limbic System: Seat of Motivation, Emotions Hypothalamus: feeding, fleeing, mating, fighting, homeostasis. Limbic system: involved in emotionality. Corpus callosum: band of axons that interconnects the hemispheres. Reticular activating system is an arousal system within the brainstem. Medulla: involved in life support functions such as respiration and heart rate. Pons: involved in respiration, sleep regulation, dreaming. Brainstem is a primitive portion of brain. Myelin is a fatty, waxy substance coating the axon of some neurons. Potential is restored when other channels open, allowing potassium ions to exit the axon. Sodium entry shifts the membrane potential toward a positive value. Ion channels open in the membrane, allowing sodium ions to enter the axon. Action potential occurs when the membrane potential rapidly shifts from -70 to +40 mV. The inside of the axon membrane is more negative that is the outside. Potassium ions are concentrated on the inside of the axon membrane. Resting Potential Sodium ions are concentrated on the outside of the axon membrane. Termination of transmitter effect (e.g. Storage and transport of NT within vesicles.







 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
